Mark Twain has been quoted as saying that he respected a person who
could spell a word more than one way. Unfortunately, Twain's enthusiasm
for creative spelling isn't widely shared today, at least in the
professional world. If you need a little help in the spelling
department, but prefer the old school way of editing text, you can turn
to Vim's spelling support.
Support for spell checking was added in Vim 7. Before that, a few scripts were available to hack spell checking support into Vim — or you could do what I did and use
If you're new to Vim and/or using Vim in text mode, it's not obvious that Vim even supports spell checking. But it does, and it's easy to use once you turn it on. You'll need to be in command mode and switch to last line mode, then run this:
You might not want to be that specific, or you might want a different region. The "en_us" specifies English, U.S. style. You might want to use "en_ca" instead, if you're in Canada, or "en_gb" for Great Britain, or "en_au" for Australia. And, of course, this works for other languages as well.
If you're using Vim to write code and prose, you might want to turn spell checking on only in the local buffer. To do that, use:
Once you've set this, Vim will highlight misspelled words. If you're using Vim in text mode, you should see the entire word highlighted, or if you're using Gvim, you should see a squiggly underline for any word that is misspelled.
Vim does more than just highlight misspelled words, it actually categorizes misspelled words, it also highlights rare words, words that aren't capitalized (but should be), and words that have the wrong spelling for the specified region. For example, I've set Vim to check for U.S. spelling (
Vim uses different colors for each type of word. This may vary depending on the colors you have set up in your terminal or how you have Gvim set up, but on my system I see misspelled words highlighted with red, an orange for rare words, blue for words that aren't capitalized, and so on.
Getting tired of seeing the highlighting? You may want to turn spell checking off if you're working with code or something like that. Use the nospell directive to turn this off:
To move to a misspelled word, use
Once the cursor is on the word, use
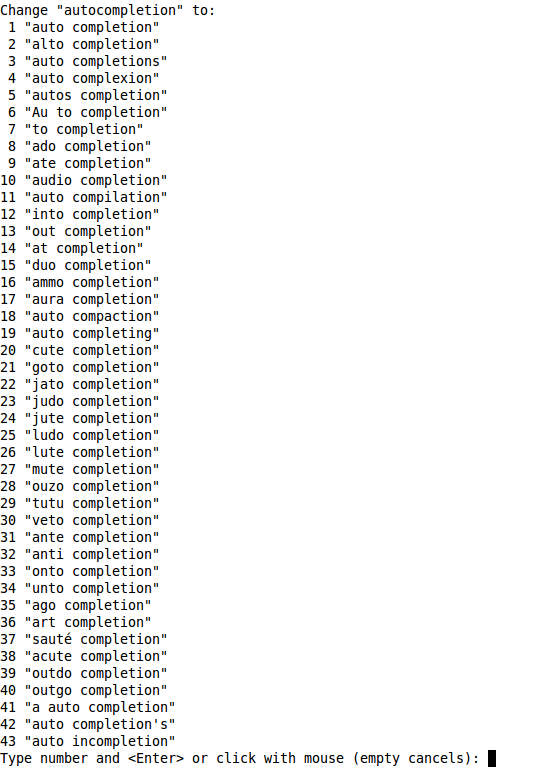
Just hit Enter if none of the suggestions work, or enter the number for the correct word.
What if Vim is wrong, and the word is correct? Use the
If you don't want to keep telling Vim explicitly every time you restart to turn on spelling, just add the following to your .vimrc:
Substitute the appropriate region, of course.
Vim's combination of syntax highlighting, autocompletion (using
Support for spell checking was added in Vim 7. Before that, a few scripts were available to hack spell checking support into Vim — or you could do what I did and use
ispell or aspell, but inline spell checking is much nicer.If you're new to Vim and/or using Vim in text mode, it's not obvious that Vim even supports spell checking. But it does, and it's easy to use once you turn it on. You'll need to be in command mode and switch to last line mode, then run this:
:set spell spelllang=en_usYou might not want to be that specific, or you might want a different region. The "en_us" specifies English, U.S. style. You might want to use "en_ca" instead, if you're in Canada, or "en_gb" for Great Britain, or "en_au" for Australia. And, of course, this works for other languages as well.
If you're using Vim to write code and prose, you might want to turn spell checking on only in the local buffer. To do that, use:
:setlocal spell spelllang=en_usOnce you've set this, Vim will highlight misspelled words. If you're using Vim in text mode, you should see the entire word highlighted, or if you're using Gvim, you should see a squiggly underline for any word that is misspelled.
Vim does more than just highlight misspelled words, it actually categorizes misspelled words, it also highlights rare words, words that aren't capitalized (but should be), and words that have the wrong spelling for the specified region. For example, I've set Vim to check for U.S. spelling (
spelllang=en_us), so it should highlight
words that are spelled correctly in another region but might be
considered incorrect for the local region.Vim uses different colors for each type of word. This may vary depending on the colors you have set up in your terminal or how you have Gvim set up, but on my system I see misspelled words highlighted with red, an orange for rare words, blue for words that aren't capitalized, and so on.
Getting tired of seeing the highlighting? You may want to turn spell checking off if you're working with code or something like that. Use the nospell directive to turn this off:
:set nospellUsing Spellchecking
Spell checking wouldn't be very useful if you didn't have any help correcting the misspelled words, or a way to tell the program that the word is actually correct. Let's start with correcting words.To move to a misspelled word, use
]s and [s. The ]s command will move the cursor to the next misspelled word, the [s command will move the cursor back through the buffer to previous misspelled words.Once the cursor is on the word, use
z=, and Vim will
suggest a list of alternatives that it thinks may be correct. For
instance, if I highlight autocompletion and then use z=, I see something like figure 1:
Just hit Enter if none of the suggestions work, or enter the number for the correct word.
What if Vim is wrong, and the word is correct? Use the
zg command and Vim will add it to its dictionary. Simple as pie. You can also mark words as incorrect using zw.If you don't want to keep telling Vim explicitly every time you restart to turn on spelling, just add the following to your .vimrc:
set spell spelllang=en_usSubstitute the appropriate region, of course.
Vim's combination of syntax highlighting, autocompletion (using
CTRL-p and CTRL-n), abbreviations and mappings,
and spell-checking makes it a killer editor to write in. Even when I
need to share materials with clients in ODF or Word format, I usually
write first in Vim with HTML and then copy and paste into
OpenOffice.org, which usually handles the formatting just fine.
Comments
Post a Comment
https://gengwg.blogspot.com/