In Python, Assignment statements do not copy objects, they create bindings between a target and an object. When we use
A copy is sometimes needed so one can change one copy without changing the other. In Python, there are two ways to create copies :
In the above code, the
Output:
Output:
Important Points:
The difference between shallow and deep copying is only relevant for compound objects (objects that contain other objects, like lists or class instances):
=
operator user thinks that this creates a new object; well, it doesn’t.
It only creates a new variable that shares the reference of the original
object. Sometimes a user wants to work with mutable objects, in order
to do that user looks for a way to create “real copies” or “clones” of
these objects. Or, sometimes a user wants copies that user can modify
without automatically modifying the original at the same time, in order
to do that we create copies of objects. A copy is sometimes needed so one can change one copy without changing the other. In Python, there are two ways to create copies :
- Deep copy
- Shallow copy
copy module. We use copy module for shallow and deep copy operations. For Example
# importing copy module import copy # initializing list 1 li1 = [1, 2, [3,5], 4] # using copy for shallow copy li2 = copy.copy(li1) # using deepcopy for deepcopy li3 = copy.deepcopy(li1) |
copy() returns a shallow copy of list and deepcopy() return a deep copy of list.Deep copy
Deep copy is a process in which the copying process occurs recursively. It means first constructing a new collection object and then recursively populating it with copies of the child objects found in the original. In case of deep copy, a copy of object is copied in other object. It means that any changes made to a copy of object do not reflect in the original object. In python, this is implemented using “deepcopy()” function.
# Python code to demonstrate copy operations # importing "copy" for copy operations import copy # initializing list 1 li1 = [1, 2, [3,5], 4] # using deepcopy to deep copy li2 = copy.deepcopy(li1) # original elements of list print ("The original elements before deep copying") for i in range(0,len(li1)): print (li1[i],end=" ") print("\r") # adding and element to new list li2[2][0] = 7 # Change is reflected in l2 print ("The new list of elements after deep copying ") for i in range(0,len( li1)): print (li2[i],end=" ") print("\r") # Change is NOT reflected in original list # as it is a deep copy print ("The original elements after deep copying") for i in range(0,len( li1)): print (li1[i],end=" ") |
The original elements before deep copying 1 2 [3, 5] 4 The new list of elements after deep copying 1 2 [7, 5] 4 The original elements after deep copying 1 2 [3, 5] 4In the above example, the change made in the list did not effect in other lists, indicating the list is deep copied.
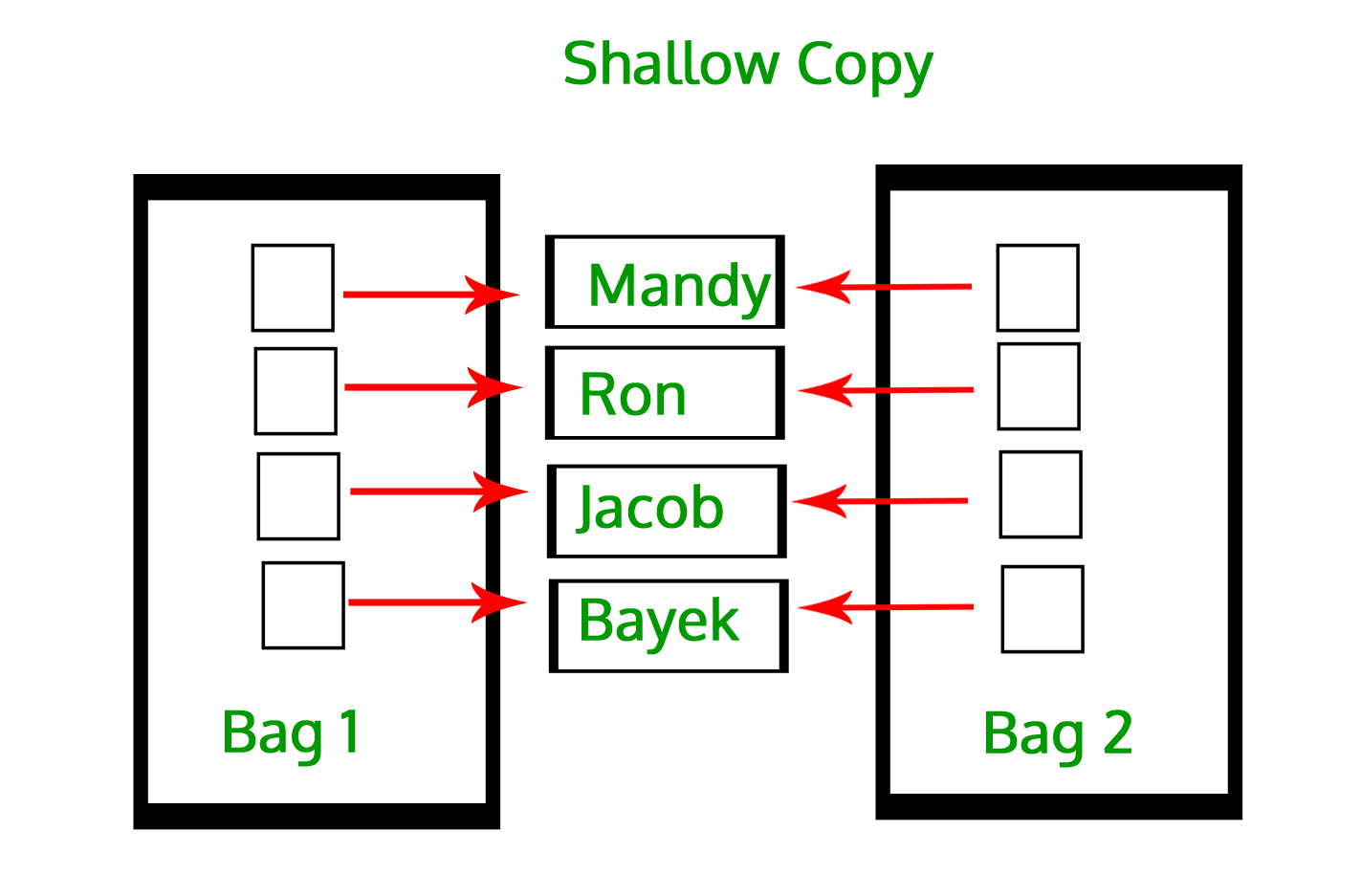
Shallow copy
A shallow copy means constructing a new collection object and then populating it with references to the child objects found in the original. The copying process does not recurse and therefore won’t create copies of the child objects themselves. In case of shallow copy, a reference of object is copied in other object. It means that any changes made to a copy of object do reflect in the original object. In python, this is implemented using “copy()” function.
# Python code to demonstrate copy operations # importing "copy" for copy operations import copy # initializing list 1 li1 = [1, 2, [3,5], 4] # using copy to shallow copy li2 = copy.copy(li1) # original elements of list print ("The original elements before shallow copying") for i in range(0,len(li1)): print (li1[i],end=" ") print("\r") # adding and element to new list li2[2][0] = 7 # checking if change is reflected print ("The original elements after shallow copying") for i in range(0,len( li1)): print (li1[i],end=" ") |
The original elements before shallow copying 1 2 [3, 5] 4 The original elements after shallow copying 1 2 [7, 5] 4In the above example, the change made in the list did effect in other list, indicating the list is shallow copied.
Important Points:
The difference between shallow and deep copying is only relevant for compound objects (objects that contain other objects, like lists or class instances):
- A shallow copy constructs a new compound object and then (to the extent possible) inserts references into it to the objects found in the original.
- A deep copy constructs a new compound object and then, recursively, inserts copies into it of the objects found in the original.

Comments
Post a Comment
https://gengwg.blogspot.com/