Most ISPs (Internet service providers) assign a dynamic IP address to the router and you can use this IP address to access your router remotely. However, the IP address can change any time and you don’t know when it changes. In this case, you might need the DDNS (Dynamic Domain Name Server) feature on the router to allow you and your friends to access your router and local servers (FTP, HTTP, etc.) using a domain name, in no need of checking and remembering the dynamic IP addresses.
TP-LINK is one of the DDNS service provider on TP-Link wireless router with cloud functions.
Here follow the steps below to set up your TP-LINK DDNS.
Step 1
Register and bind your TP-Link cloud account to the TP-Link wireless router. For how to, please click here.
Step2
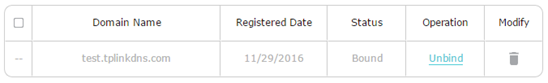
Go to Advance > Network > Dynamic DNS. Select TP-LINK as the DDNS service provider. Click Register, enter a hostname to create your own domain name, for example, test.tplinkdns.com. Then just click Save and the domain name will be bound to your router automatically.

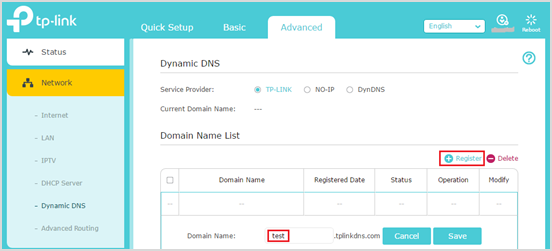

Notes:
- Make sure you have internet when you’re registering a TP-LINK domain name.
- If you fail to register a TP-LINK domain name, it means your domain name has been registered by others. Please try to change another hostname.
- Your domain name will be bound to the external public IP address of your network. So don’t worry if the ISP assigns a private WAN IP address (such as 192.168.1.x) to the router.
- If you want to change the domain name, just click Unbind and Delete your current domain name. Then tap Register to bind a new one.
Comments
Post a Comment
https://gengwg.blogspot.com/