Understanding the basic terms and parts of Azure Pipelines helps you further explore how it can help you deliver better code more efficiently and reliably.
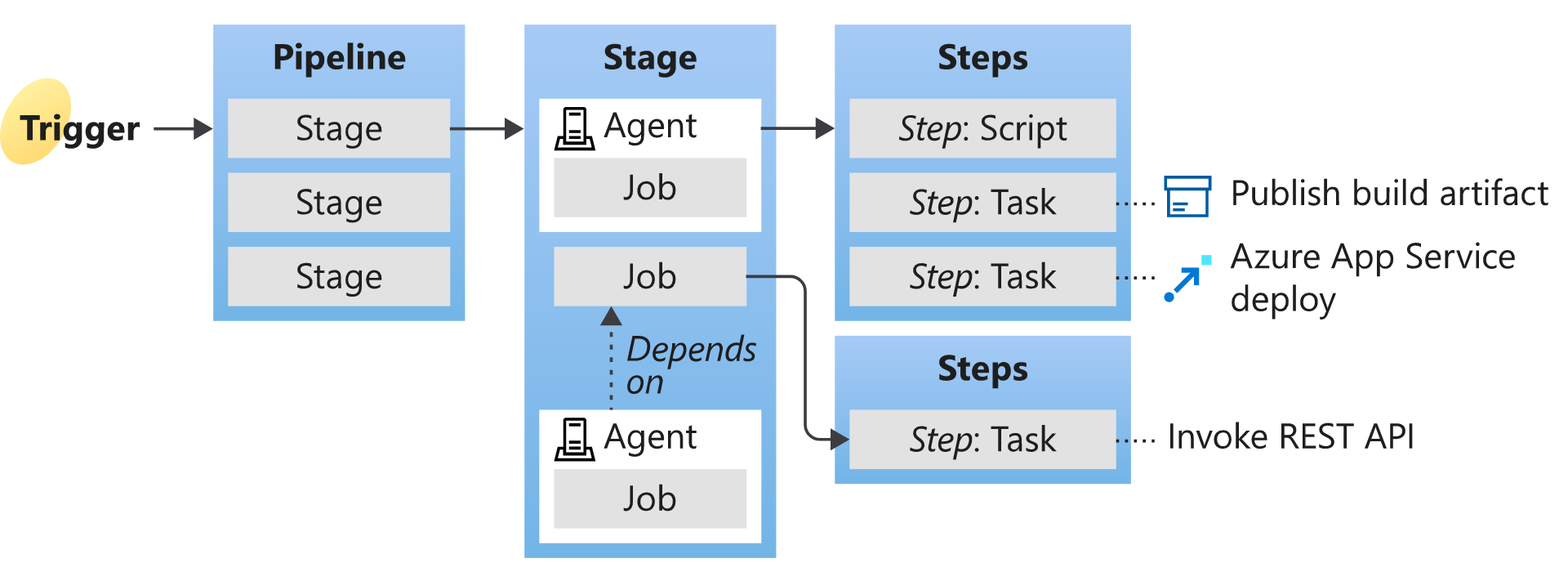
Agent
When your build or deployment runs, the system begins one or more jobs. An agent is installable software that runs a build or deployment job.
Artifact
An artifact is a collection of files or packages published by a build. Artifacts are made available for the tasks, such as distribution or deployment.
Build
A build represents one execution of a pipeline. It collects the logs associated with running the steps and the test results.
Continuous delivery
Continuous delivery (CD) (also known as Continuous Deployment) is a process by which code is built, tested, and deployed to one or more test and production stages. Deploying and testing in multiple stages helps drive quality. Continuous integration systems produce deployable artifacts, which include infrastructure and apps. Automated release pipelines consume these artifacts to release new versions and fix existing systems. Monitoring and alerting systems constantly run to drive visibility into the entire CD process. This process ensures that errors are caught often and early.
Continuous integration
Continuous integration (CI) is the practice used by development teams to simplify the testing and building of code. CI helps to catch bugs or problems early in the development cycle, making them more accessible and faster to fix. Automated tests and builds are run as part of the CI process. The process can run on a schedule, whenever code is pushed, or both. Items known as artifacts are produced from CI systems. The continuous delivery release pipelines use them to drive automatic deployments.
Deployment target
A deployment target is a virtual machine, container, web app, or any service used to host the developed application. A pipeline might deploy the app to one or more deployment targets after the build is completed and tests are run.
Job
A build contains one or more jobs. Most jobs run on an agent. A job represents an execution boundary of a set of steps. All the steps run together on the same agent.
For example, you might build two configurations - x86 and x64. In this case, you have one build and two jobs.
Pipeline
A pipeline defines the continuous integration and deployment process for your app. It's made up of steps called tasks.
It can be thought of as a script that describes how your test, build, and deployment steps are run.
Release
When you use the visual designer, you can create a release or a build pipeline. A release is a term used to describe one execution of a release pipeline. It's made up of deployments to multiple stages.
Stage
Stages are the primary divisions in a pipeline: "build the app," "run integration tests," and "deploy to user acceptance testing" are good examples of stages.
Task
A task is the building block of a pipeline. For example, a build pipeline might consist of build and test tasks. A release pipeline consists of deployment tasks. Each task runs a specific job in the pipeline.
Trigger
A trigger is set up to tell the pipeline when to run. You can configure a pipeline to run upon a push to a repository at scheduled times or upon completing another build. All these actions are known as triggers.
Comments
Post a Comment
https://gengwg.blogspot.com/