在计算机科学里,树的遍历(也称为树的搜索)是图的遍历的一种,指的是按照某种规则,不重复地访问某种树的所有节点的过程。具体的访问操作可能是检查节点的值、更新节点的值等。不同的遍历方式,其访问节点的顺序是不一样的。以下虽然描述的是二叉树的遍历算法,但它们也适用于其他树形结构。
由于从给定的某个节点出发,有多个可以前往的下一个节点(树不是线性数据结构),所以在顺序计算(即非并行计算)的情况下,只能推迟对某些节点的访问——即以某种方式保存起来以便稍后再访问。常见的做法是采用栈(LIFO)或队列(FIFO)。由于树本身是一种自我引用(即递归定义)的数据结构,因此很自然也可以用递归方式,或者更准确地说,用corecursion,来实现延迟节点的保存。这时(采用递归的情况)这些节点被保存在call stack中。
遍历方式的命名,源于其访问节点的顺序。最简单的划分:是深度优先(先访问子节点,再访问父节点,最后是第二个子节点)?还是广度优先(先访问第一个子节点,再访问第二个子节点,最后访问父节点)? 深度优先可进一步按照根节点相对于左右子节点的访问先后来划分。如果把左节点和右节点的位置固定不动,那么根节点放在左节点的左边,称为前序(pre-order)、根节点放在左节点和右节点的中间,称为中序(in-order)、根节点放在右节点的右边,称为后序(post-order)。对广度优先而言,遍历没有前序中序后序之分:给定一组已排序的子节点,其“广度优先”的遍历只有一种唯一的结果。
其C代码如下:
其C代码如下
其C代码如下
目录
遍历的种类
与那些基本上都有标准遍历方式(通常是按线性顺序)的线性数据结构(如链表、一维数组)所不同的是,树结构有多种不同的遍历方式。从二叉树的根节点出发,节点的遍历分为三个主要步骤:对当前节点进行操作(称为“访问”节点)、遍历左边子节点、遍历右边子节点。这三个步骤的先后顺序也是不同遍历方式的根本区别。由于从给定的某个节点出发,有多个可以前往的下一个节点(树不是线性数据结构),所以在顺序计算(即非并行计算)的情况下,只能推迟对某些节点的访问——即以某种方式保存起来以便稍后再访问。常见的做法是采用栈(LIFO)或队列(FIFO)。由于树本身是一种自我引用(即递归定义)的数据结构,因此很自然也可以用递归方式,或者更准确地说,用corecursion,来实现延迟节点的保存。这时(采用递归的情况)这些节点被保存在call stack中。
遍历方式的命名,源于其访问节点的顺序。最简单的划分:是深度优先(先访问子节点,再访问父节点,最后是第二个子节点)?还是广度优先(先访问第一个子节点,再访问第二个子节点,最后访问父节点)? 深度优先可进一步按照根节点相对于左右子节点的访问先后来划分。如果把左节点和右节点的位置固定不动,那么根节点放在左节点的左边,称为前序(pre-order)、根节点放在左节点和右节点的中间,称为中序(in-order)、根节点放在右节点的右边,称为后序(post-order)。对广度优先而言,遍历没有前序中序后序之分:给定一组已排序的子节点,其“广度优先”的遍历只有一种唯一的结果。
深度优先遍历
以下均是用递归方法。先序遍历(Pre-Order Traversal)
指先访问根,然后访问子树的遍历方式
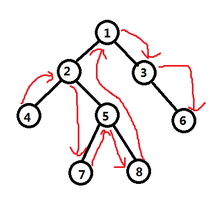
深度优先遍历 - 前序遍历
void pre_order_traversal(TreeNode *root) {
// Do Something with root
if (root->lchild != NULL)
pre_order_traversal(root->lchild);
if (root->rchild != NULL)
pre_order_traversal(root->rchild);
}
中序遍历(In-Order Traversal)
指先访问左(右)子树,然后访问根,最后访问右(左)子树的遍历方式
深度优先遍历 - 中序遍历
void in_order_traversal(TreeNode *root) {
if (root->lchild != NULL)
in_order_traversal(root->lchild);
// Do Something with root
if (root->rchild != NULL)
in_order_traversal(root->rchild);
}
后序遍历(Post-Order Traversal)
指先访问子树,然后访问根的遍历方式
深度优先搜索 - 后序遍历
void post_order_traversal(TreeNode *root) {
if (root->lchild != NULL)
post_order_traversal(root->lchild);
if (root->rchild != NULL)
post_order_traversal(root->rchild);
// Do Something with root
}
广度优先遍历
和深度优先遍历不同,广度优先遍历会先访问离根节点最近的节点。二叉树的广度优先遍历又称按层次遍历。算法借助队列实现。
广度优先遍历 - 层次遍历
void Layer_Traver(tree *root) {
int head = 0, tail = 0;
tree *p[SIZE] = {NULL};
tree *tmp;
if (root != NULL) {
p[head] = root;
tail++;
// Do Something with p[head]
} else
return;
while (head < tail) {
tmp = p[head];
// Do Something with p[head]
if (tmp->left != NULL) { // left
p[tail] = tmp->left;
tail++;
}
if (tmp->right != NULL) { // right
p[tail] = tmp->right;
tail++;
}
head++;
}
return;
}
多叉树的遍历
深度优先遍历
先访问根结点,后选择一子结点访问并访问该节点的子结点,持续深入后再依序访问其他子树,可以轻易用递回或栈的方式实现。void travel(treenode* nd){
for(treenode* nex : nd->childs){ // childs 存放指向其每個子結點的指標
travel(nex);
}
return;
}



Comments
Post a Comment
https://gengwg.blogspot.com/