If you were searching information on an IP address such as 192.168.1.1 or 10.0.0.1, you're on the right page. Because you're about to learn something that confuses almost anyone trying learning about IP addresses.
But if you read on, you'll see it doesn't have to be confusing.
This article is about what private IP addresses are. Before you learn about private IP addresses, you will also need to know about public IP addresses, which you should know a little about already if you're reading this article. Lucky for you, that's something fairly easy to explain.
The IP address you see on our home page—that looks like this—161.170.193.104, is an example of a public IP address. If you've ever wondered "what is a public IP," now you know. It's that simple.
Now, about that other kind of IP address...
What's a Private IP address?
Home routers have their local address set to a default, private IP address number. It's usually the same address for the other models from that manufacturer, and it can be seen in the manufacturer's documentation.
Who knew?
 Actually, you should welcome your private IP
Actually, you should welcome your private IP
Here's a look at the default private (also called "local") IP addresses for popular brands of routers:
- Linksys routers use 192.168.1.1
- D-Link and NETGEAR routers are set to 192.168.0.1
- Cisco routers use either 192.168.10.2, 192.168.1.254 or 192.168.1.1
- Belkin and SMC routers often use 192.168.2.1
Let's go back to public IP addresses for a second...
How you connect to the world.
You're public IP address is the IP address that someone on the other end of your Internet activity would see (if they bothered to look for it). That's the only reason it's known as a public IP address.

The Internet works similarly, except it directs your personal activity (emails, answers to Google inquiries, etc.), and forwards the electronic messages to your computer's address.
You couldn't do much without a public IP address. It's your passport to the Internet.
Public and Private. Working together to get you connected.
In theory, your computer must have its own unique IP address so that it will only receive the information that is meant for you.

However, that's not how it works out, because of one major exception—network computers that are linked to a router and share the same public IP address.
Yes. If you have a router, you have a private IP address.
And here's how it works...
Reserved for private networks.
The organizations that distribute IP addresses to the world reserves a range of IP addresses for private networks.
- 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 (65,536 IP addresses)
- 172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255 (1,048,576 IP addresses)
- 10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255 (16,777,216 IP addresses)
Your simple home network, with its router at the center and computers connected to it—wired or wireless—classifies as one of those networks.
Your router—once it makes its Internet connection through your Internet Service Provider—sends Internet activity to any computer connected to your router, and is the basis of a networking innovation called a Network Address Translation (NAT).
- NAT is a process in which your router changes your private IP Address into a public one so that it can send your traffic over the Internet, keeping track of the changes in the process.
- When the information comes back to your router, it reverses the change—from a real IP address into a private one—and forwards the traffic back to your computer.
In other words, the router connects to the other devices (usually desktops, laptops and tablets).
 Your private IP is just that. Private.
Your private IP is just that. Private.
The private address ranges in a network don't have to be synchronized with the rest of the world and Internet.
As a matter of fact, the private address range can be used by more than one address. A network administrator using these private addresses has more room for subnetting, and many more assignable addresses.
The private IP address does one job for your home network.
These blocks of addresses can be used by a private network. Even if your neighbor is using the exact same addresses, it won't cause a problem, because that's HIS or HER network, not yours.
Don't let that confuse you.
You see, these private addresses are known as non-routable addresses. The networking on the Internet routes Internet activity connected to your public IP address only, not your private IP.
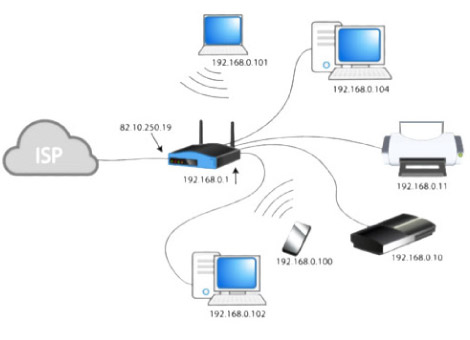 How Private and public IP addresses work together.
How Private and public IP addresses work together.Four key takeaways
To wrap up our discussion about public and private IP addresses, keep these four ideas in mind:

Private IP addresses are untracked and unrestricted. WhatIsMyIPaddess.com cannot geographically locate a user's computer by their private IP address.

It is perfectly normal to see traffic from these numbers if you have a small home or office network. By default, most routers and access points use these numbers to assign to your local computers. It is most likely these numbers represent computers on your own internal network.

If you see these numbers in the headers of an unsolicited email, they usually indicate transit between servers within a corporate network or ISP. Again, they are not useful in identifying the origin of an email. In such cases, you can usually find the true origin by looking for the earliest "Received" mail header.

The traffic does not come from the IANA (the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority), a non-government, Internet-specific organization that gives out (assigns and allocates) IP addresses. As the authority for IP addresses, they do not use or operate them, and they are not the source of the traffic.
Comments
Post a Comment
https://gengwg.blogspot.com/