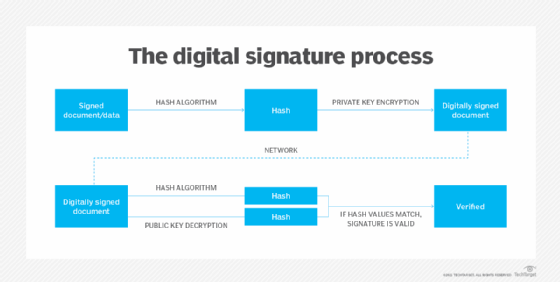
To create a digital signature, signing software, such as an email program, is used to provide a one-way hash of the electronic data to be signed.
A hash is a fixed-length string of letters and numbers generated by an algorithm. The digital signature creator's private key is then used to encrypt the hash. The encrypted hash -- along with other information, such as the hashing algorithm -- is the digital signature.
The reason for encrypting the hash instead of the entire message or document is a hash function can convert an arbitrary input into a fixed-length value, which is usually much shorter. This saves time as hashing is much faster than signing.
The value of a hash is unique to the hashed data. Any change in the data, even a change in a single character, will result in a different value. This attribute enables others to use the signer's public key to decrypt the hash to validate the integrity of the data.
If the decrypted hash matches a second computed hash of the same data, it proves that the data hasn't changed since it was signed. If the two hashes don't match, the data has either been tampered with in some way and is compromised or the signature was created with a private key that doesn't correspond to the public key presented by the signer -- an issue with authentication.
A digital signature can be used with any kind of message, whether it is encrypted or not, simply so the receiver can be sure of the sender's identity and the message arrived intact. Digital signatures make it difficult for the signer to deny having signed something as the digital signature is unique to both the document and the signer and it binds them together. This property is called nonrepudiation.
Digital signatures are not to be confused with digital certificates. A digital certificate is an electronic document that contains the digital signature of the issuing CA. It binds together a public key with an identity and can be used to verify that a public key belongs to a particular person or entity.
Most modern email programs support the use of digital signatures and digital certificates, making it easy to sign any outgoing emails and validate digitally signed incoming messages. Digital signatures are also used extensively to provide proof of authenticity, data integrity and nonrepudiation of communications and transactions conducted over the internet.
Comments
Post a Comment
https://gengwg.blogspot.com/