Continuous security validation should be added at each step from development through production to help ensure the application is always secure.
This approach aims to switch the conversation with the security team from approving each release to consenting to the CI/CD process and monitor and audit the process at any time.
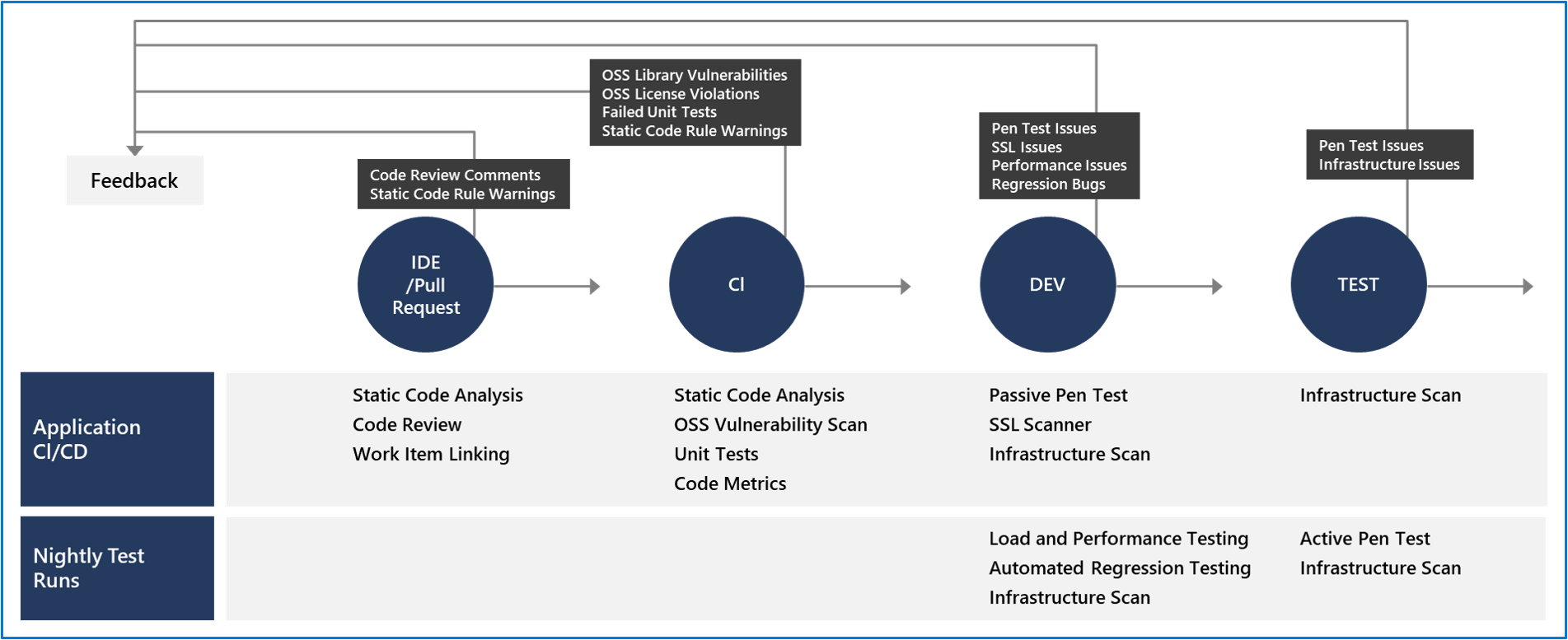
The diagram below highlights the critical validation points in the CI/CD pipeline when building green field applications.
You may gradually implement the tools depending on your platform and your application's lifecycle.
Especially if your product is mature and you haven't previously run any security validation against your site or application.
IDE / pull request
Validation in the CI/CD begins before the developer commits their code.
Static code analysis tools in the IDE provide the first line of defense to help ensure that security vulnerabilities aren't introduced into the CI/CD process.
The process for committing code into a central repository should have controls to help prevent security vulnerabilities from being introduced.
Using Git source control in Azure DevOps with branch policies provides a gated commit experience that can provide this validation.
Enabling branch policies on the shared branch requires a pull request to start the merge process and ensure the execution of all defined controls.
The pull request should require a code review, the one manual but important check for identifying new issues introduced into your code.
Along with this manual check, commits should be linked to work items for auditing why the code change was made and require a continuous integration (CI) build process to succeed before the push can be completed.
Today, developers don't hesitate to use components available in public package sources (such as npm or NuGet).
With faster delivery and better productivity, open-source software (OSS) components are encouraged across many organizations.
However, as the dependency on these third-party OSS components increases, the risk of security vulnerabilities or hidden license requirements also increases compliance issues.
For a business, it's critical, as issues related to compliance, liabilities, and customer personal data can cause many privacy and security concerns.
Identifying such issues early in the release cycle gives you an advanced warning and enough time to fix the problems. Notably, the cost of rectifying issues is lower the earlier the project discovers the problem.
Many tools can scan for these vulnerabilities within the build and release pipelines.
Once the merge is complete, the CI build should execute as part of the pull request (PR-CI) process.
Typically, the primary difference between the two runs is that the PR-CI process doesn't need any packaging/staging in the CI build.
These CI builds should run static code analysis tests to ensure that the code follows all rules for both maintenance and security.
Several tools can be used for it:
- SonarQube.
- Visual Studio Code Analysis and the Roslyn Security Analyzers.
- Checkmarx - A Static Application Security Testing (SAST) tool.
- BinSkim - A binary static analysis tool that provides security and correctness results for Windows portable executables and many more.
Many of the tools seamlessly integrate into the Azure Pipelines build process. Visit the Visual Studio Marketplace for more information on the integration capabilities of these tools.
Also, to verify code quality with the CI build, two other tedious or ignored validations are scanning third-party packages for vulnerabilities and OSS license usage.
The response is fear or uncertainty when we ask about third-party package vulnerabilities and licenses.
Organizations trying to manage third-party packages vulnerabilities or OSS licenses explain that their process is tedious and manual.
Fortunately, Mend Software's tools can make this identification process almost instantaneous.
In a later module, we'll discuss integrating several helpful and commonly used security and compliance tools.
Comments
Post a Comment
https://gengwg.blogspot.com/